Traits
Agouti (Default)
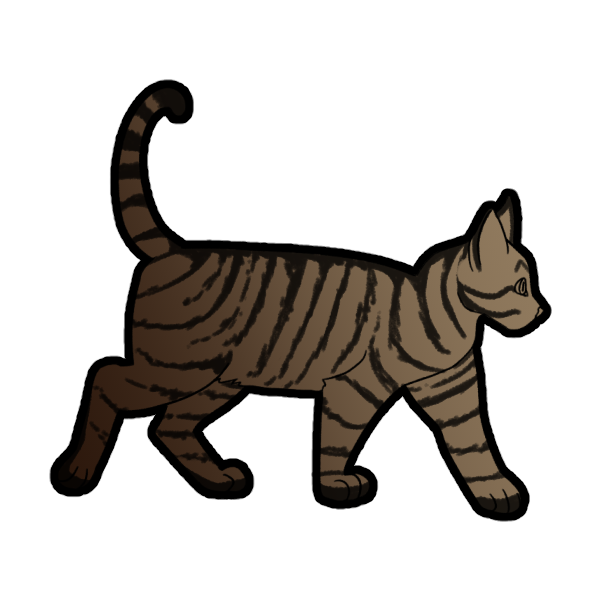
The Agouti gene controls the color banding in a cat’s fur. In Pigmented cats, Solid still presents with tabby markings, but these can be made more subtle for artistic interpretation.
This gene determines whether a cat is Tabby (AA or Aa) or Solid (aa). Tabby is dominant over Solid.
Design Note: A Black cat with Tabby will present as a Brown cat with Black striping.
See also: Charcoal
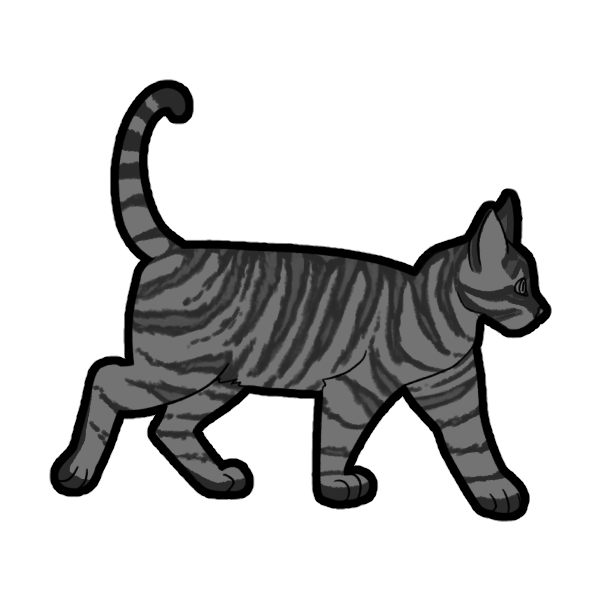
Tabby (Default)
There are two default varieties of Tabby that can be further modified by other genes.
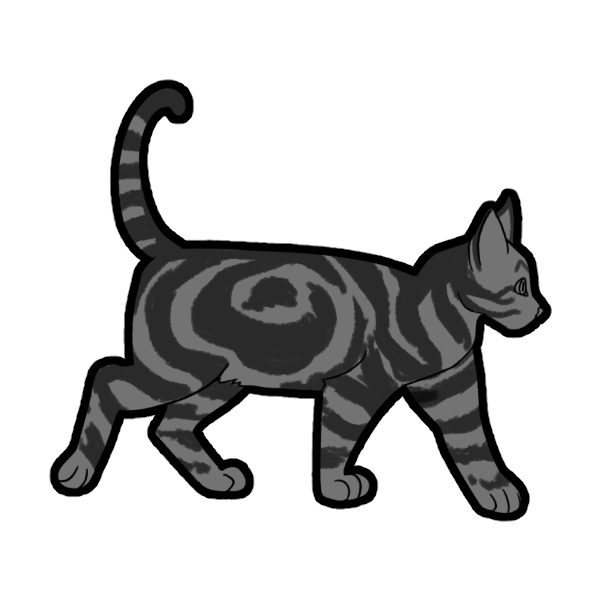
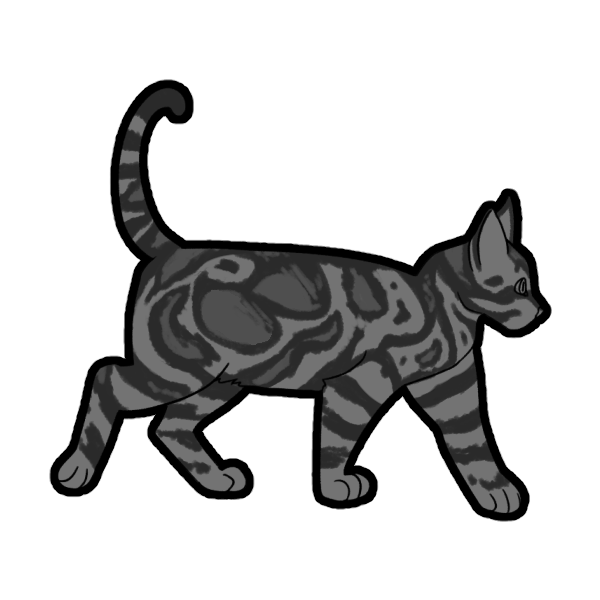
Tabby comes in Mackerel (McMc/Mcmc) or Classic (mcmc). Mackerel is thinner striping that typically runs perpendicular to the fur, whereas Classic is thicker, more swirled striping.
Charcoal (Basic)
There is a rare Agouti variation called Charcoal (APbAPb), which is partially dominant over Solid (aa), and will only present if there is no dominant Tabby (AA). Charcoal is a darkening and bleeding of the tabby markings especially around the face and back striping, producing a more striking contrast between the base coat and the tabby markings.
Examples:
- APbAPb: Charcoal
- aa: Solid
- AAPb: Tabby carrying Charcoal
- APba: Charcoal carrying Solid.
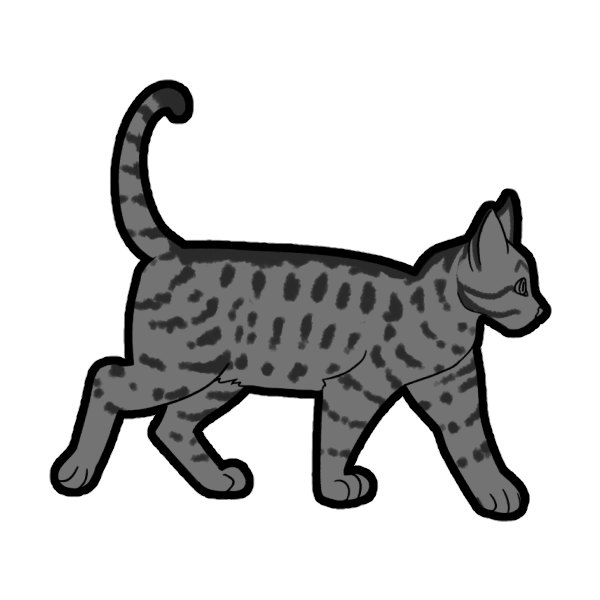
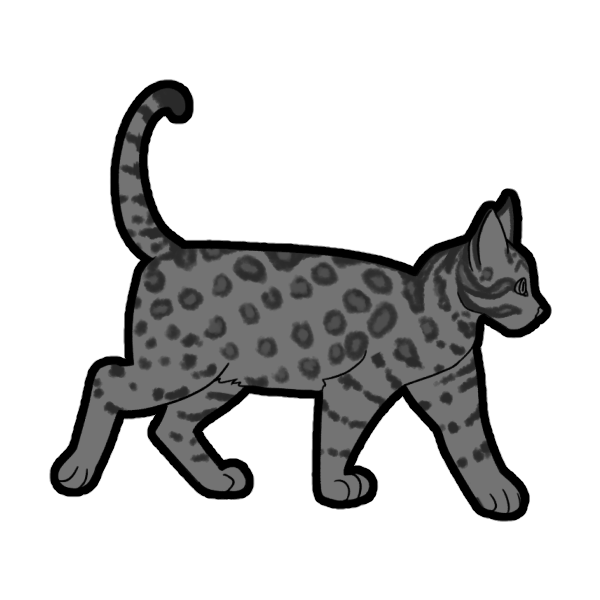
Spotted (Basic)
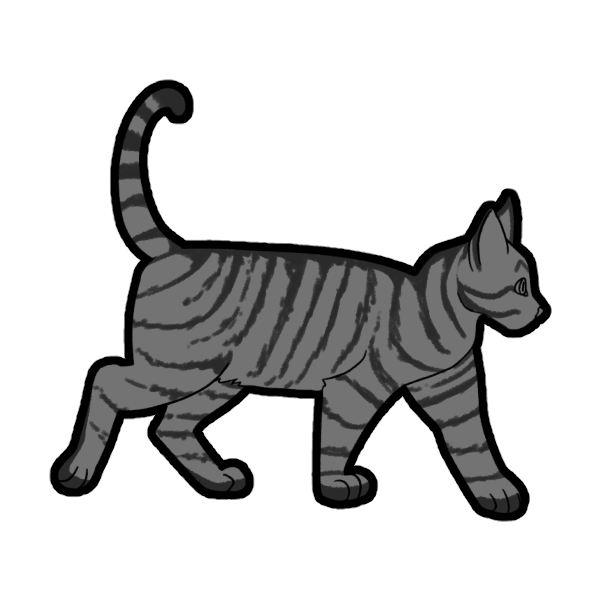
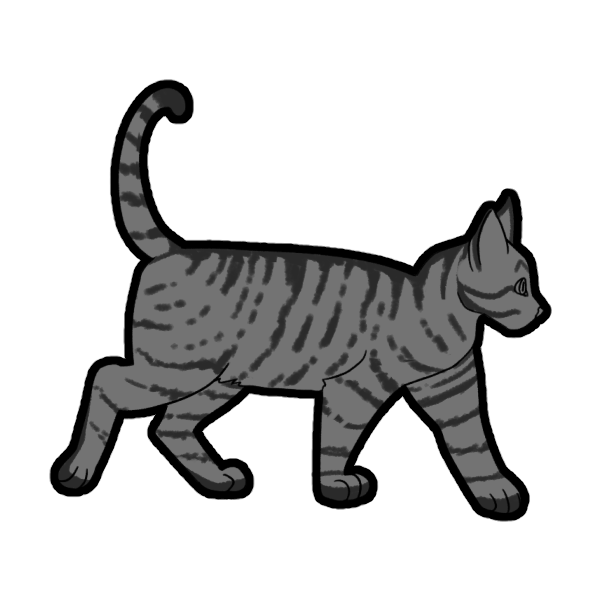
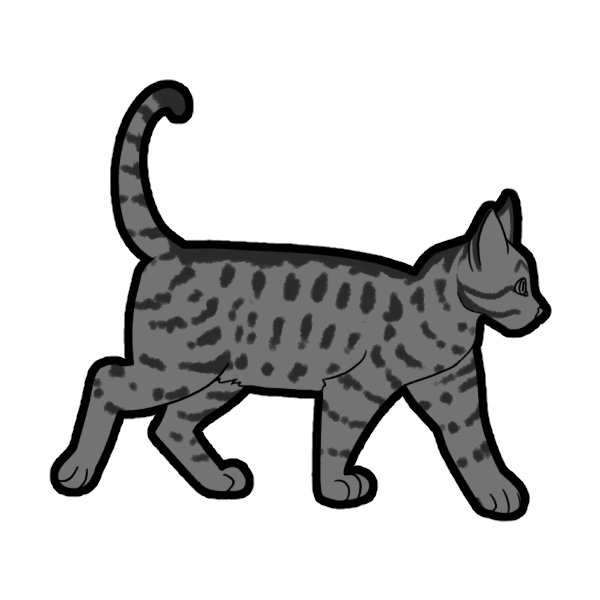
Spotted (SpSp or Spsp) is a dominant gene that breaks Mackerel Tabby stripes into spots. A cat with only one copy of this gene will have their tabby stripes broken up, refered to as Broken Tabby, but not fully spotted.
Only visible on Mackerel cats, though Classic cats can be carriers.
Examples:
- spsp: Normal Tabby
- Spsp: Broken Tabby
- SpSp: Spotted Tabby
Normal Tabby vs. Broken Tabby vs. Spotted Tabby



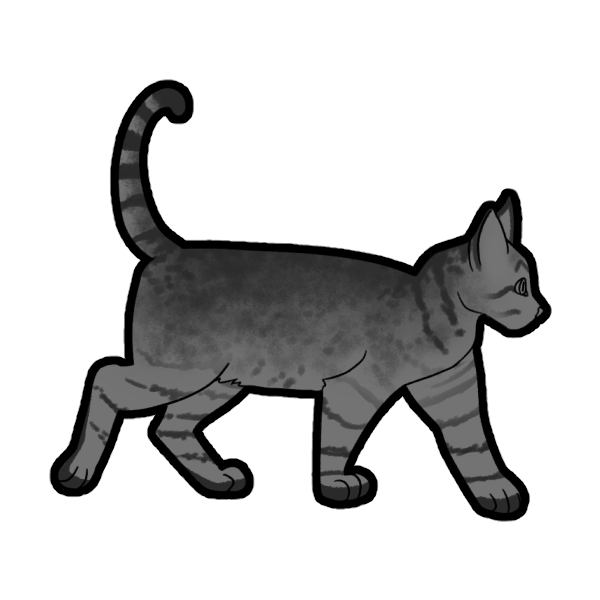
Ticked (Basic)
Ticked (TT or Tt) is a dominant gene that overrides any Tabby pattern with Ticking, usually presented as fine speckling on the main body. Face markings remain untouched, and some striping may still occur on the neck, legs, and tail.
Heterozygous Ticked (Tt) may optionally "mask" less of the the Tabby pattern underneath it.
Examples:
- McMcTt: (Het) Ticked Mackerel Tabby
- mcmcTt: (Het) Ticked Classic Tabby
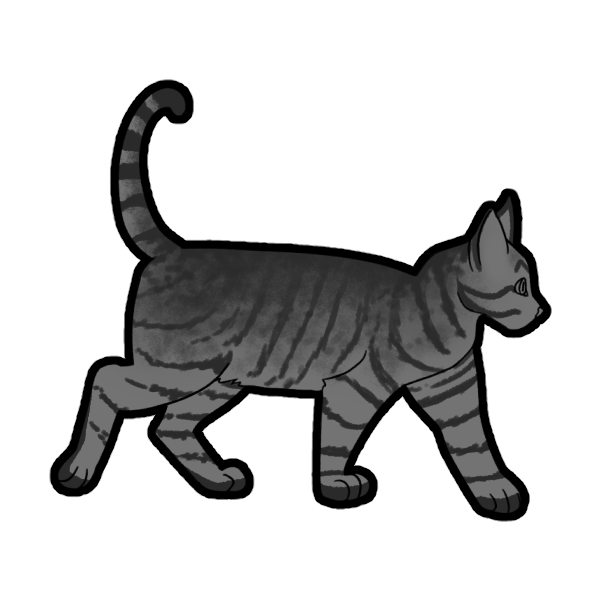
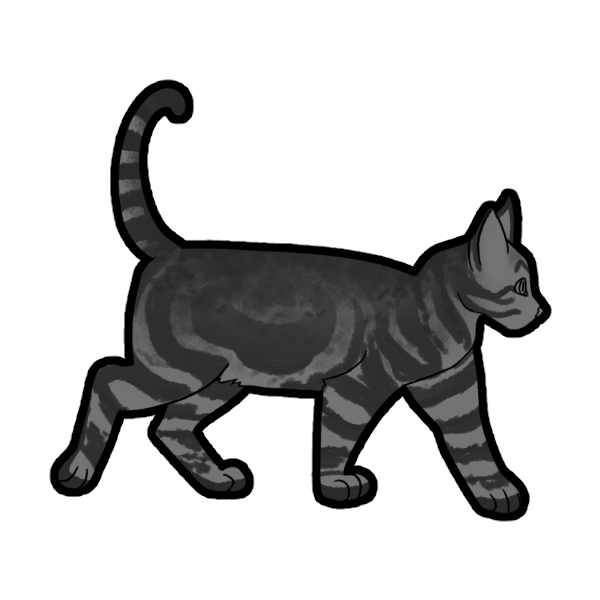


Tabby Modifer: Bengal (Basic)
The Bengal Modifier (BmBm or Bmbm) is a dominant gene that alters Tabby markings. It turns the tabby markings into a two-tone marking and generally looks more like wild cat markings. Turns Mackerel into Braided, Classic into Marble, and Spotted into Rosettes.
Examples:
- McMcBmBm: Braided, aka Mackerel Modified
- mcmcBmBm: Marbled, aka Classic Modified
- McMcSpSpBmBm: Rosettes, Aka Spotted Modified
Edge cases: - mcmcSpSpBmBm: Marbled (Rosettes Carried due to Spotted only modifying Mackerel)
- McmcBmBm: Braided (Marbled Carried)
- McMcSpsp: Braided/Rosettes mixture, Broken Mackerel Modified.
- McmcSpspBmBm: Braided/Rosettes mixture carying Marble!
Braided (Mackerel) vs. Marbled (Classic) vs. Rosettes (Spotted)



Roan (Basic)
Also known as Karpati, Roan (KK/Kk) is a Dominant gene that causes a cat to be born with extra white hairs that darken over time.
Roan cats can become fully colored with only occasional white speckling, present as salt and pepper (black/gray with white speckling), or present white points (like an inverse Siamese/Colorpoint.)
White Spotting (Basic)
White genes overlap all other markings. There are several different kinds of white genes.
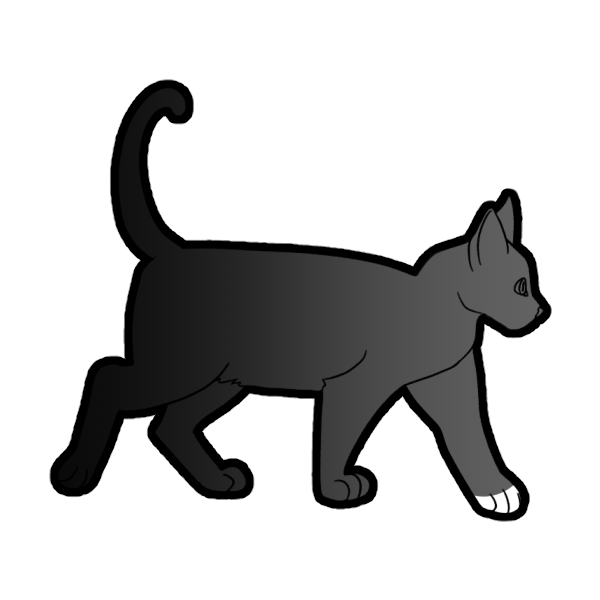
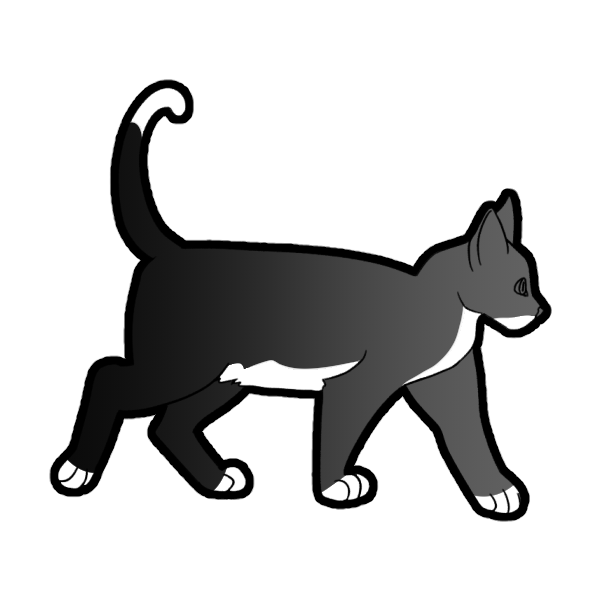
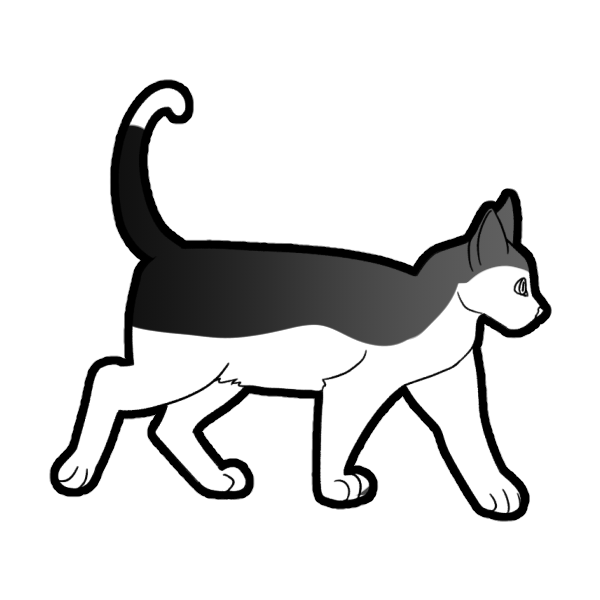
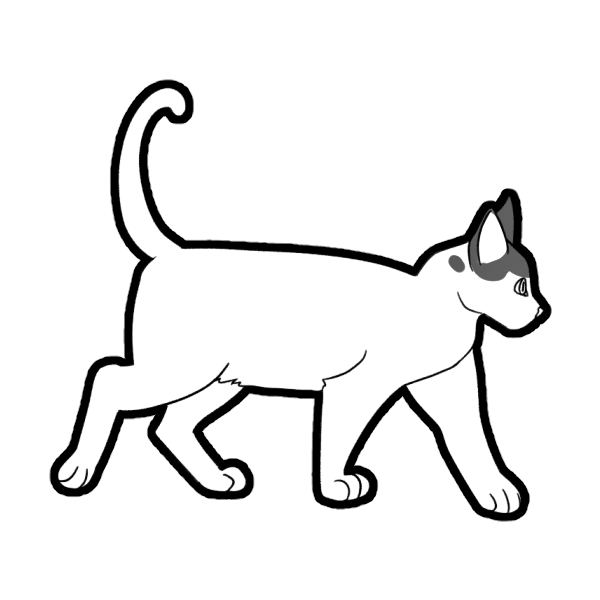
White Spotting is the most common white gene. A cat can either have no white (ww), low white spotting (WSw which has 1-50% coverage) and high white spotting (WSWS which has 51-100% coverage).
These are basic ranges for Low Spotting (Left 2) and High Spotting (Right Two). These are only guidelines to give you a rough idea of how much a cat with White Spotting should have.
See Also: Dominant White, White Spotting, White Gloves, Albino
Dominant White (Basic)
White genes overlap all other markings. There are several different kinds of white genes.
Dominant White (WDWD, WDw, WDW, WDwg) is a dominant gene (surprise!), that presents as a 100% white cat, covering all markings. These cats often have blue eyes and are more likely to be deaf than their counterparts, but are not required to have either.
See Also: White Spotting, White Gloves, Albino
White Gloves (Basic)
White genes overlap all other markings. There are several different kinds of white genes.
White Gloves (wgwg) is a recessive gene that results in white paws. A carrier of this gene that also has White Spotting will have white paws and optionally any amount of white spotting, while a cat who has two copies of this gene will only show white on their paws.
Examples:
- ww - No white (unless Albino is present)
- wgw - No white
- wgwg - White gloves
- WSwg- White Spotting with White Gloves
- WDwg- Dominant White carrying White Glove
See Also: White Spotting, Dominant White, Albino